How to Turn On DRM [For Chrome, Firefox, Edge & More]
![How to Turn On DRM [For Chrome, Firefox, Edge & More]](https://foyercus.blob.core.windows.net/287a2408185e68c371c/blog/305/c/9381e0c8-3e63-416a-a87f-6f000e3158e7.jpg)
![How to Turn On DRM [For Chrome, Firefox, Edge & More]](https://foyercus.blob.core.windows.net/287a2408185e68c371c/blog/305/c/9381e0c8-3e63-416a-a87f-6f000e3158e7.jpg)
Running into issues with content not playing in a web browser can be frustrating, especially when it's due to Digital Rights Management (DRM).
If you've stumbled upon a problem where some content (like a video) won't play, and you see a "DRM must be enabled" or "please turn on DRM in this browser" error, you're in the right place.
In this guide, I'll will walk you through the process of enabling DRM in Chrome for just about every browser including Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Brave, and Opera.
Turning on DRM for any browser will only take a minute. All you have to do is find one setting, and doesn't require any admin rights.
So let's get right into how to turn on DRM so you can get back to that content you're trying to view.
How to Turn On DRM on Chrome
Turning on DRM within Chrome is easy. All you need to do is:
- Navigate to "Privacy and Security" settings. You can paste this in your address bar to get there quickly:
chrome://settings/content
- You can also get here by clicking the 3 dots on the top right, then clicking "Settings", and choosing "Privacy and Security" settings on the left.
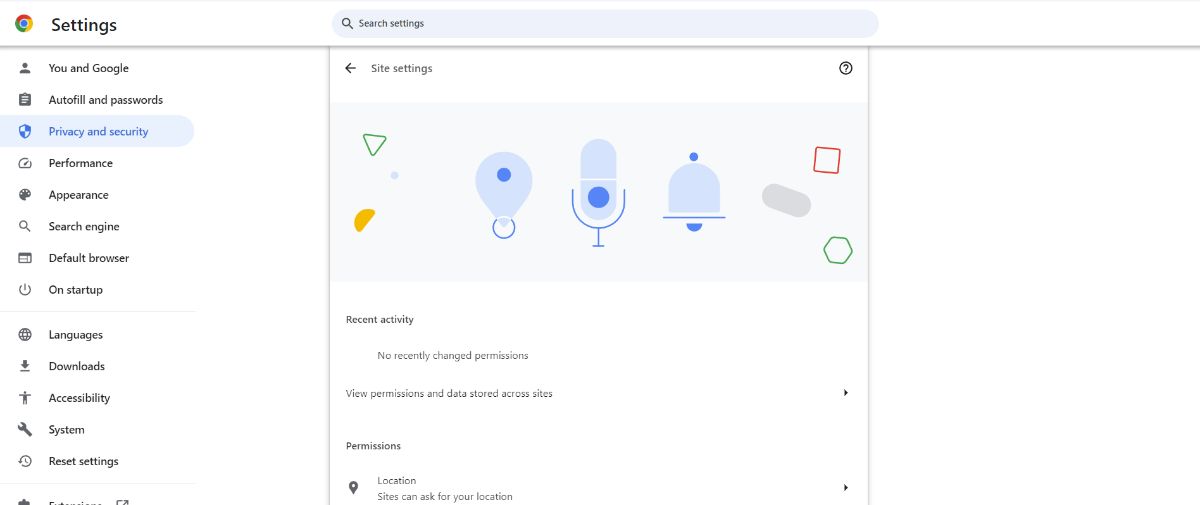
- Click on "Additional content settings"
- Click "Protected content IDs"
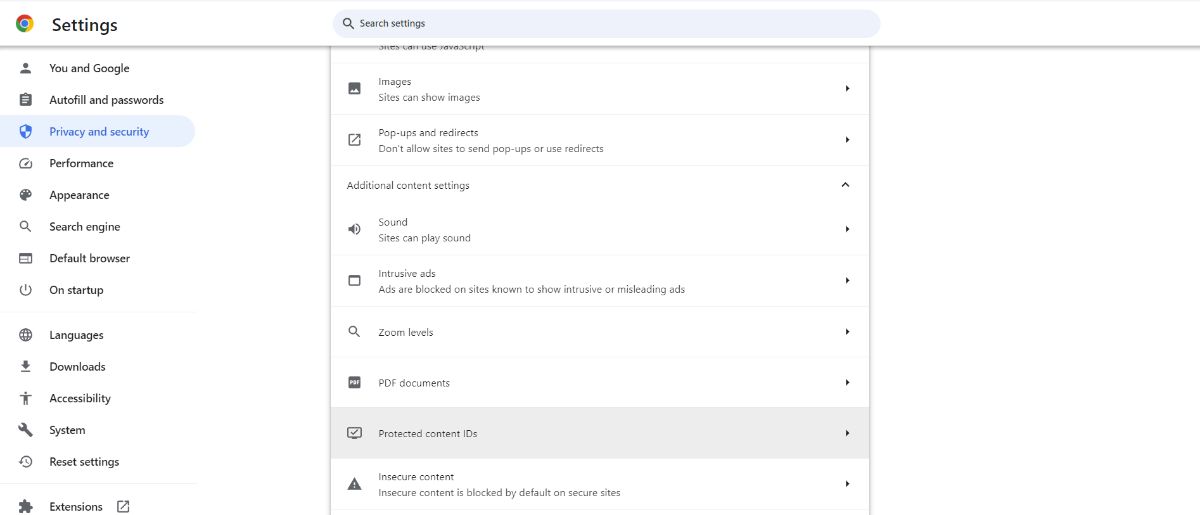
- Click "Sites can play protected content"
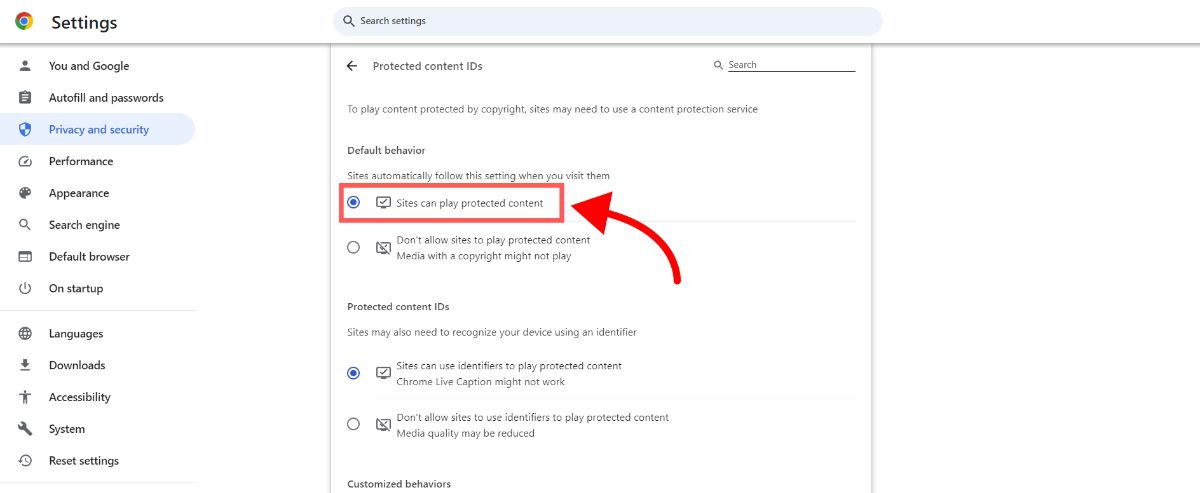
That's it! Now you will be able to view content and watch videos that are protected via DRM in Chrome.
How to Turn On DRM on Firefox
To turn on DRM in Firefox:
- Navigate to the "Settings" page. You can paste this link into your address bar to get there quickly:
about:preferences
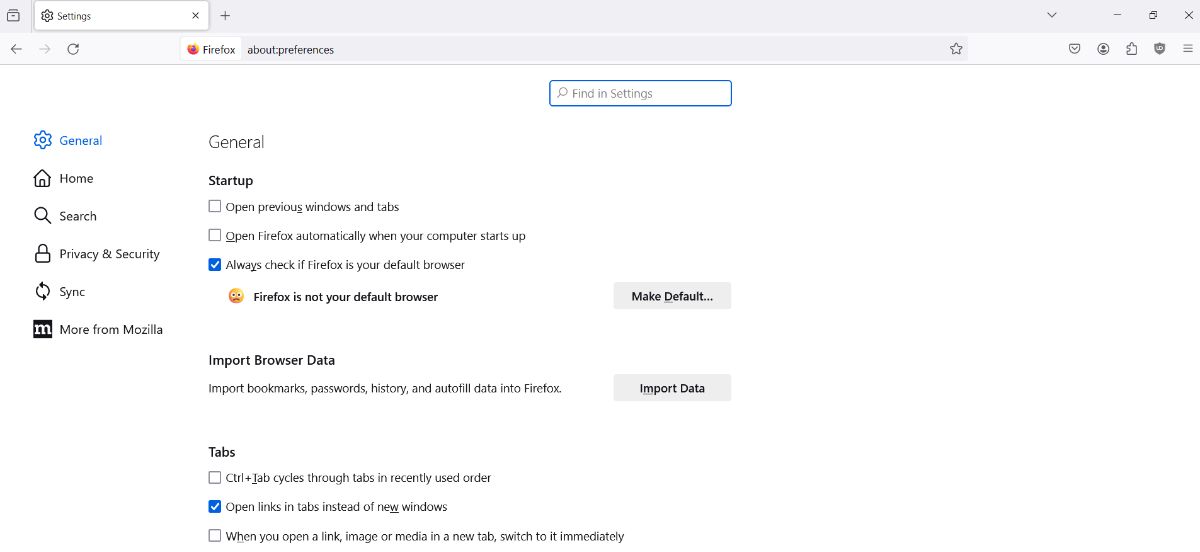
- Scroll down until you see the "Digital Right Management (DRM) Content" section
- Make sure "Play DRM-controlled content" is enabled
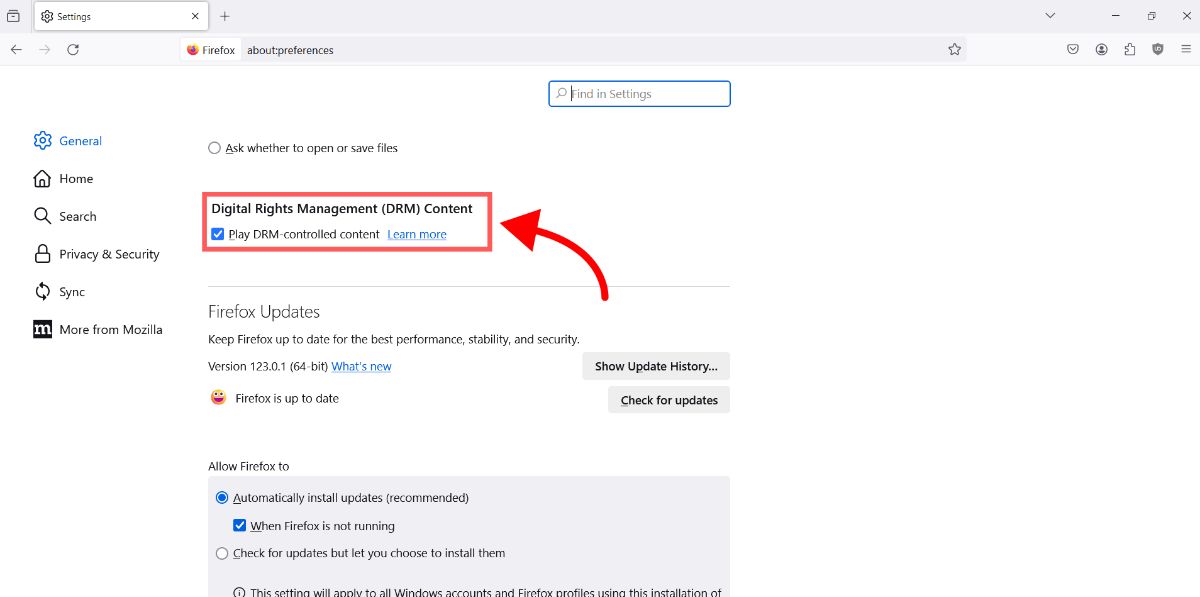 That's it! If the "Play DRM-controlled content" checkbox is enabled, you should be able to view DRM content in Firefox.
That's it! If the "Play DRM-controlled content" checkbox is enabled, you should be able to view DRM content in Firefox.
How to Turn On DRM for Microsoft Edge
Microsoft Edge supports DRM content natively, using Microsoft's PlayReady and Google's Widevine CDMs. To enable DRM in Edge:
- Paste this link into your address bar to get to the setting:
edge://settings/content/protectedContent
- To get there manually, click on the 3 dots on the top right of the browser, and navigate to the "Cookies and site permissions" menu item on the left.
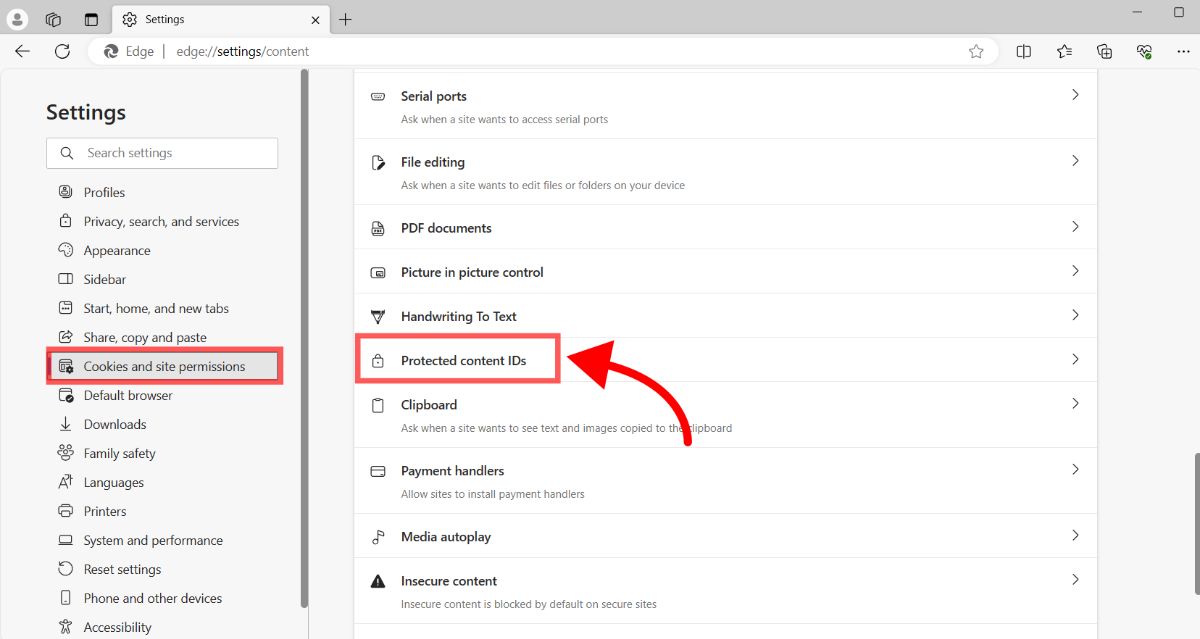
- Make sure "Allow sites to play protected content (recommended)" is enabled.
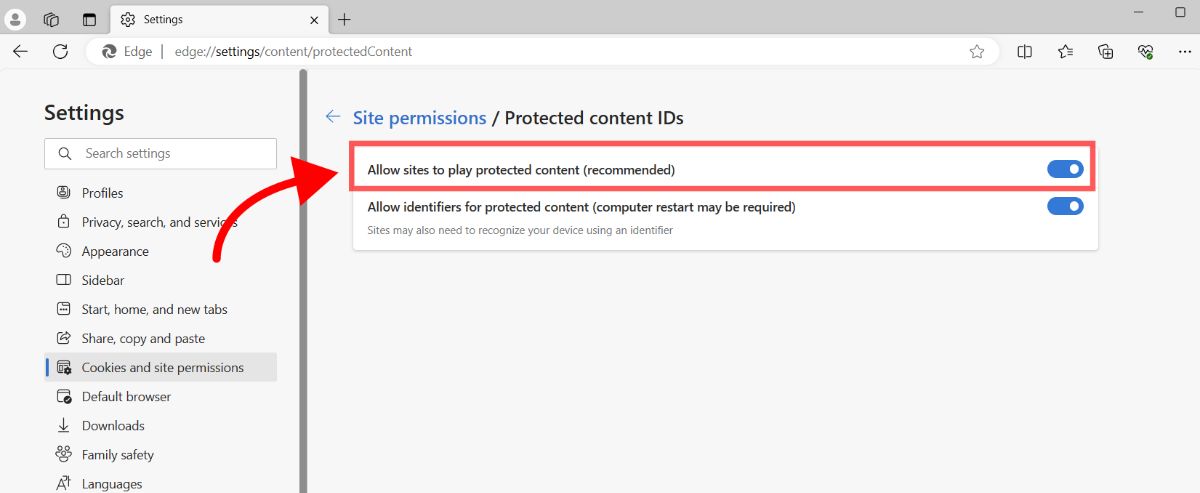 That's it! You will now be able to play content protected with DRM in Microsoft Edge.
That's it! You will now be able to play content protected with DRM in Microsoft Edge.
How to Turn On DRM for Opera
Opera browser includes support for Widevine, enabling users to view DRM-protected content. To check or modify DRM settings:
- Access Opera Settings: Press
ALT+Pon your keyboard or click on the Opera menu and select "Settings." - Find Privacy & Security: Scroll down or use the search bar to find the "Privacy & security" section.
- Enable DRM Content: Look for a setting related to protected content or Widevine and ensure it is enabled. Opera usually handles DRM permissions and installations automatically when you attempt to play DRM-protected content.
How to Turn on DRM for Brave
Brave browser supports DRM content through Google Widevine CDM. To enable DRM in Brave:
- Open Brave Settings: Click on the menu button and select "Settings."
- Navigate to Extensions: Find the "Extensions" section on the left-hand menu.
- Enable Widevine: Toggle the "Widevine" option to enable it. Brave may prompt you to enable Widevine the first time you visit a site that requires DRM.
How to Fix a "DRM" Error (If Enabling DRM Didn't Work)
When you've ensured that Digital Rights Management (DRM) settings are correctly enabled on your browser or device but still encounter problems playing DRM-protected content, it's time to consider other potential issues. Here are several factors that could be interfering with your ability to access and enjoy DRM-protected media:
1. Outdated Software
Ensure that your browser, operating system, and any relevant applications are up to date. Software updates often include fixes for security issues, improvements to DRM handling, and compatibility enhancements that can resolve playback issues.
2. Browser Extensions or Add-ons
Some browser extensions, particularly ad blockers or privacy-focused add-ons, can interfere with the proper functioning of DRM-protected content. Try disabling extensions one by one to identify if any are causing the problem. Alternatively, try playing the content in an incognito or private browsing window, where most extensions are disabled by default.
3. Network Restrictions
Certain networks, especially those in educational institutions, workplaces, or public Wi-Fi hotspots, may have firewalls or other restrictions that block the transmission of DRM-protected content. If possible, try accessing the content using a different network to see if this resolves the issue.
4. Hardware Limitations
Some DRM content requires hardware support for content protection technologies like HDCP (High-bandwidth Digital Content Protection). If your display, graphics card, or cable does not support the required DRM standards, you may be unable to play protected content. This is particularly relevant for high-definition or ultra-high-definition video.
5. Incorrect System Time
DRM systems often rely on the correct system time to authenticate and play content. Ensure your device’s clock is accurately set to the current date and time for your time zone. Incorrect system time can lead to authentication errors that prevent DRM content from playing.
6. Corrupted Media Licenses or Cache
Sometimes, the licenses stored on your device for playing DRM-protected content can become corrupted, or your browser's cache can interfere with content playback. Clearing your browser's cache and cookies or resetting DRM licenses in your media player’s settings can sometimes resolve these issues.
7. Conflicting Software
Other software on your device, such as VPNs (Virtual Private Networks), screen recording tools, or software that alters or monitors network traffic, can interfere with DRM content playback. Try disabling such software to determine if it is causing the problem.
8. Insufficient User Rights
On computers, especially those in a workplace, you may not have the necessary user permissions to install or run the DRM components required for content playback. Contact your IT department or system administrator to ensure you have the appropriate rights or to request assistance.
To get to the root of the problem, its good to understand the basics.
So let's get a little bit into what exactly DRM is, and a few types of DRM (like Google Widevine).
This could help you know what questions to ask to troubleshoot further.
What is DRM?
Digital Rights Management (DRM) is a set of access control technologies used by publishers, copyright holders, and hardware manufacturers to impose limitations on the usage of digital content and devices. At its core, DRM is designed to prevent unauthorized reproduction and distribution of copyrighted material, ensuring that only legitimate, paying customers can access and use digital media. This encompasses a wide array of content, including ebooks, music, movies, and software.
What's the Purpose of DRM?
The primary goal of DRM is to protect the intellectual property rights of content creators and distributors. It helps in securing revenue for those who invest time, money, and effort into producing digital content. By controlling how a piece of media can be accessed, copied, and shared, DRM systems aim to combat piracy and unauthorized distribution, which can significantly impact the profitability and viability of digital media projects.
How Does DRM Work?
DRM systems function by encrypting the content and then providing keys to unlock it only under certain conditions. These conditions can vary widely but often include restrictions such as:
- Limiting the number of devices on which content can be accessed or the number of times content can be played.
- Controlling the ability to copy, edit, or share the content.
- Setting expiration dates on content or access periods.
When you purchase or access DRM-protected content, the DRM system checks if you meet the set conditions before allowing you to view, play, or use the content. This process is usually transparent to the user, aiming to balance content protection with ease of use.
What are the Issues with DRM?
While DRM is essential for protecting copyrights and ensuring creators are compensated for their work, it has faced criticism for several reasons:
- User Restrictions: Some argue that DRM overly restricts legitimate users, complicating access to purchased content across different devices or platforms.
- Privacy Concerns: DRM systems sometimes require online authentication, raising concerns about user privacy and data collection.
- Interoperability Issues: DRM can lead to compatibility problems, where content purchased on one platform or device cannot be accessed on another, limiting consumer choice and flexibility.
What is Google Widevine?
Google Widevine is a leading digital rights management (DRM) technology used to securely license, distribute, and protect playback of content on any consumer device. Widevine enables content creators, service providers, and hardware manufacturers to deliver video content securely to their audience, regardless of the device or platform.
How Google Widevine Works
Widevine operates by providing a content decryption module (CDM) that works across a multitude of platforms and devices, including desktop browsers, smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and gaming consoles. This flexibility makes it an ideal solution for content providers who wish to reach a broad audience without worrying about device compatibility or security breaches.
The technology supports various DRM schemes, offering robust protection for content through encryption, secure key exchange, and licensing policies. This ensures that only authorized users can access and view the content, helping to prevent piracy and unauthorized sharing.
Where is Widevine Used?
Widevine is widely adopted by major streaming platforms and content providers around the globe. Its technology is used by services like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Disney+, Hulu, and many others to securely stream video content to millions of users. Widevine's compatibility with multiple browsers, including Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera, ensures a seamless viewing experience for users, regardless of their preferred browser.
In browsers like Firefox, Widevine CDM is downloaded and enabled by default to facilitate smooth playback of DRM-controlled content. It operates in a secure, sandboxed environment, enhancing user security by isolating the DRM process from the rest of the browser's operations. Users are notified when Widevine CDM is in use, maintaining transparency and control over their browsing experience.
Conclusion
Hopefully now that your browser has DRM enabled you should be able to watch that protected content.
If you're still running into issues, remember there are a few options to try like updating your browser, and disabling extensions. You can also try using a different browser!
Thanks for reading! If you have any comments or feedback, please send a comment below.


